Introduction
In mathematics, a metric space is a set where a distance (called a metric) is defined between elements of the set. Metric space methods have been employed for decades in various applications, for example in internet search engines, image classification, or protein classification. For general background information on metric spaces, please refer to this Wikipedia page.
In petroleum reservoir modeling, metric space methods are not widely known, and few applications of metric space methods have been presented. Most all the work using Metric Spaces has come from the Stanford Center For Reservoir Forecasting under guidance of Prof. J. Caers. The slow adoption is likely due to the fact that the vast majority of reservoir modeling studies are performed using a single (static) reservoir model, which is calibrated to historical data and then used for analysis and decision making. In such cases, there is no possibility to quantify the uncertainty in the forecast that comes comes from the uncertainty associated with the input: geology, initilization, PVT, relative permeabilities, etc.
Overview
Metric space methods are best employed to analyze and interpret a group (ensemble) of reservoir models and are attractive methods for uncertainty studies or sensitivity analysis when a (large) ensemble of reservoir models is used.
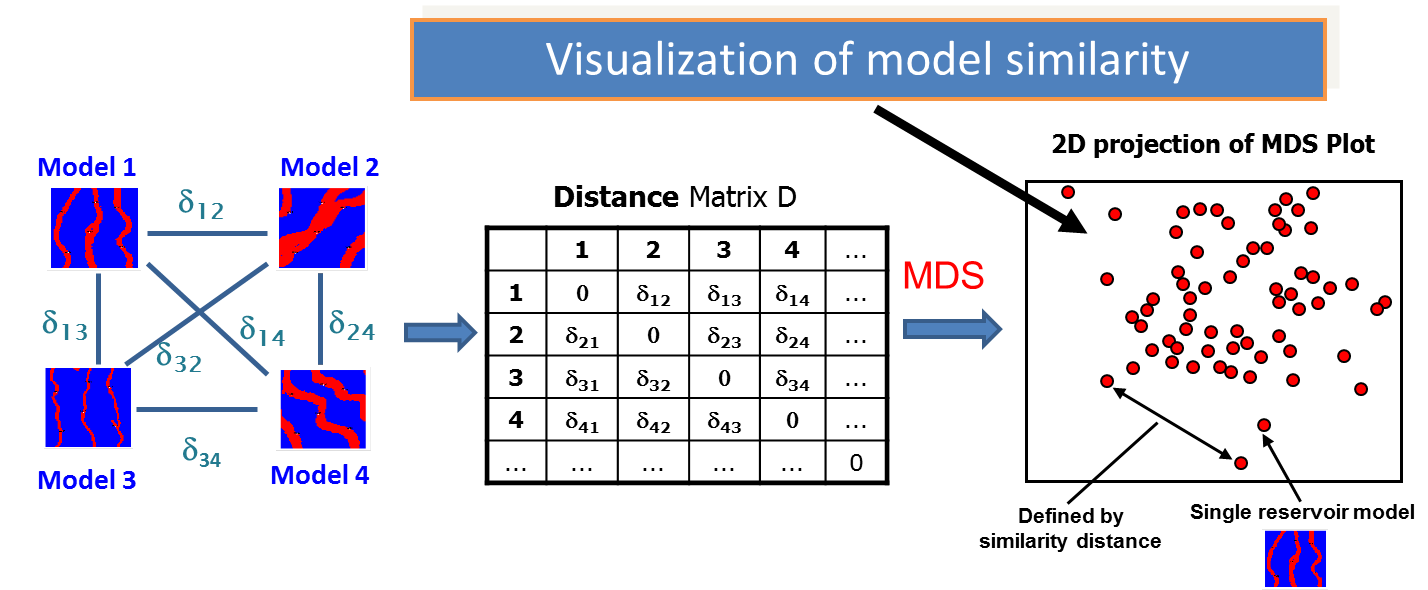
A metric space (MS) in reservoir modeling is defined by a dissimilarity distance which measures the dissimilarity between pairs of reservoir models, shown schematically in the figure below (left). The distance measure applied over all model pairs forms a distance matrix shown in the figure below (center). The distance matrix defines the metric space. The metric space can be visualized using multi-dimensional scaling (MDS), whose output is shown in the figure below (right). MDS takes the distance matrix, and translates the models into points in a Euclidean space that can be visualized. The location of the points (models) in Euclidean space are optimized to best approximate the distances in the distance matrix. The MDS plot is a visual and diagnostic tool. MDS is a dimensionality reduction technique, similar to PCA.
Visualization of Model Similarity
As is illustrated, the distribution of the models in Euclidean space provides a visualization of the model similarity - models close to each other in MDS space are similar in terms of the distance measure. Those models far from each other are dissimilar in terms of the distance measure.